
Dark Sky Glossary
We have listed below the definitions for a number of the basic terms and words used in the fields of dark sky, lighting, and astronomy. These definitions pertain only in those contexts and may have other or additional meanings in other fields. Some of these terms are fairly technical, so we have tried our best to make them understandable for the non-technical person.
A
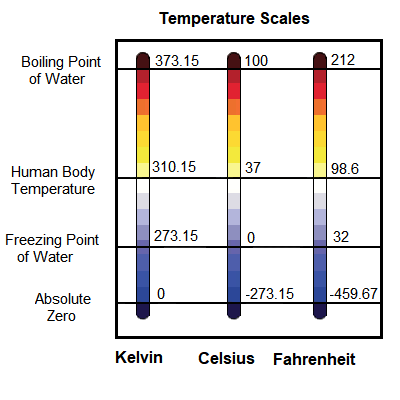 absolute zero – The lowest temperature that is theoretically possible, completely absent of all heat, and the point at which the motion of atoms completely stops. It is zero on the Kelvin scale, equal to -273.15°C or -459.67°F. Although no one has achieved absolute zero, scientists have reached within a few millionths of Kelvin above absolute zero.
absolute zero – The lowest temperature that is theoretically possible, completely absent of all heat, and the point at which the motion of atoms completely stops. It is zero on the Kelvin scale, equal to -273.15°C or -459.67°F. Although no one has achieved absolute zero, scientists have reached within a few millionths of Kelvin above absolute zero.
accent lighting – Lighting used to emphasize or draw attention to a special object or building.
adaptive controls – Devices such as motion sensors, timers, and dimmers used with outdoor lighting equipment to vary the intensity or duration of operation of lighting.
ALA – American Lighting Association.
ambient light – The general overall level of lighting in an area.
American Lighting Association (ALA) – A trade association covering the US, Canada, and the Caribbean, concerned about residential lighting, with members including manufacturers, event organizers, and designers.
angstrom – A unit of length, equal to one hundred-millionth of a centimeter, 10-10 meter or 0.1 nanometer, used mainly to express wavelengths often used in astronomy.
architectural lighting – Lighting that is primarily decorative in nature and designed into a building and its construction. It also provides ambient lighting as a secondary function.
arc lamp – A lamp that creates an electric arc between two electrodes. Gas-discharge lamps are arc light that stimulate a gas, causing it to glow, generating an output of light.
astronomy – The science that studies the universe outside the earth's atmosphere, such as the sun, moon, stars, planets, comets, galaxies, and other heavenly bodies and phenomena.
average rated life – See lamp life.
B
baffle – An opaque or translucent element to shield a light source from direct view.
ballast – A device used with certain types of lamps to achieve the necessary voltage, current, and/or waveform for starting and operating the lamp.
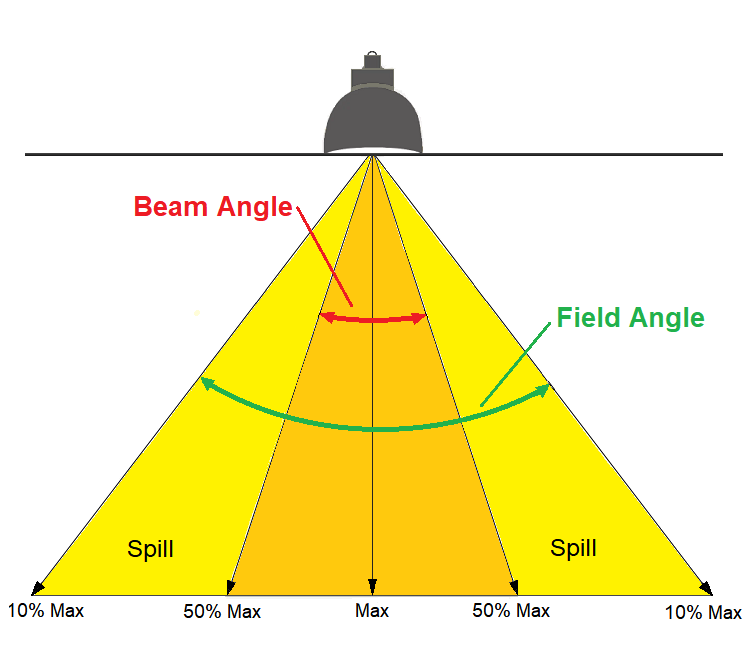 beam angle – The angle that describes the downward light cone emitted by a lighting fixture with a reflector. The angle is measured between the downward direction, where the lamp provides maximum lighting intensity, and the direction in which the intensity drops to 50%. A lamp with a larger angle spread provides its lighting into a wider cone. Also called beam spread. The field angle is measured to the point at which the intensity drops to 10%, which indicates how far the light reaches until it essentially fades into the darkness. See also cutoff angle.
beam angle – The angle that describes the downward light cone emitted by a lighting fixture with a reflector. The angle is measured between the downward direction, where the lamp provides maximum lighting intensity, and the direction in which the intensity drops to 50%. A lamp with a larger angle spread provides its lighting into a wider cone. Also called beam spread. The field angle is measured to the point at which the intensity drops to 10%, which indicates how far the light reaches until it essentially fades into the darkness. See also cutoff angle.
beam spread – See beam angle.
Bortle scale – A semi-quantitative measure of the brightness of the night sky based on visual observations. Classes are whole numbers between 1 and 9 with several criteria for each level. It was developed by astronomer John Bortle.
Bortle Scale |
|
Class |
Description |
| 1 | Excellent dark-sky site |
| 2 | Typical truly dark site |
| 3 | Rural sky |
| 4 | Rural/suburban transition |
| 5 | Suburban sky |
| 6 | Bright suburban sky |
| 7 | Suburban/urban transition |
| 8 | City sky |
| 9 | Inner-city sky |
brightness – As used in lighting facts, the amount of light emitted from a light bulb, measured in lumens. Brightness is sometimes called light output or light intensity. Brightness is also used as a qualitative term for the light emitted from a surface, which should more properly be called illuminance.
bright white – See light bulb color ranges.
bulb – The transparent casing that contains a light source, usually made of glass. LED lights sometimes emulate the look of an incandescent bulb with a casing made of glass or plastic. See also light bulb.
C
candela (cd) – Unit of luminous intensity. One candela is one lumen per steradian. Formerly called the candle.
candlepower – Luminous intensity expressed in candelas.
candlepower distribution curve – A plot of the variation in luminous intensity of a lamp or luminaire.
canopy – The part of a luminaire that covers the outlet box and wiring connections. Canopies can be decorative.
CCT – Correlated Color Temperature.
CFL – Compact Fluorescent Lamp.
CIE – Commission Internationale de l’Eclairagea.
circadian – Biological processes that recur naturally on a twenty-four-hour cycle.
coefficient of utilization (CU) – Ratio of luminous flux (lumens) from a luminaire received on the “work plane” (the area where the light is needed) to the lumens emitted by the luminaire.
color rendering – Effect of a light source on the color appearance of objects in comparison with their color appearance under normal day light.
color rendering index (CRI) – A measure of the accuracy with which a light source of a particular CCT renders different colors in comparison to a reference light source with the same CCT. A high CRI provides better illumination with the same or lower lighting levels. It is important not to mix lamps with different CCTs and CRIs. Specify both the CCT and CRI when purchasing lamps.
Commission Internationale de l’Eclairage (CIE) – The International Commission on Illumination. The international authority on light, illumination, and color, which sets most lighting standards.
compact fluorescent lamp (CFL) – A type of fluorescent lamp specifically designed to replace an incandescent light bulb and to fit into light fixtures designed for incandescent bulbs. The lamp life is about ten times longer and use about one-fifth of the energy of incandescent light bulbs.
cones and rods – Groups of light-sensitive cells in the retinas of the eyes of humans and animals. Cones dominate the response when the luminance level is high, and provide color perception. Rods dominate at low luminance levels, but give no significant color perception.
conspicuity – The capacity of a signal to stand out in relation to its background so as to be readily discovered by the eye (as in lettering on a sign, for example).
constellation – A group of stars in the night sky that have a recognizable pattern, traditionally named for a mythological figure or by its apparent shape. Modern astronomers have divided the sky into eighty-eight constellations with defined boundaries.
correlated color temperature (CCT) – A measure of warmness or coolness of a light, expressed on the Kelvin scale. Lamps with a CCT of less than 3,200 K are pinkish and considered warm. Lamps with a CCT greater than 4,000 K are bluish-white and considered cool.
 cosine law – Lambert's cosine law states that the luminous intensity reflecting from a surface is proportional to the cosine of the angle between the direction of the incident light and the surface. See also inverse-square law.
cosine law – Lambert's cosine law states that the luminous intensity reflecting from a surface is proportional to the cosine of the angle between the direction of the incident light and the surface. See also inverse-square law.
CRI – Color Rendering Index.
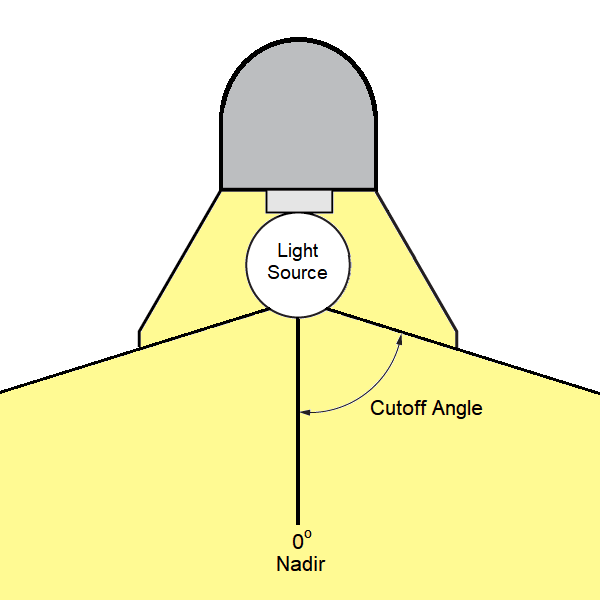
cutoff angle – The angle of a luminaire, measured up from the nadir (i.e. straight down), between the vertical axis and the first line of sight at which the bare source (the bulb or lamp) is not visible.
cutoff fixture – Defined by the IES as “Intensity at or above 90° (horizontal) no more than 2.5% of lamp lumens, and no more than 10% of lamp lumens at or above 80°;”
D
dark adaptation – The process by which the eye becomes adapted to a luminance less than about 0.03 candela per square meter (0.01 footlambert).
dark side of the moon – (1) Dark Side of the Moon, an album by the English rock band Pink Floyd. (2) An incorrect description often used to refer to the hemisphere of the Moon that is not visible from Earth. However, it is lit by sunlight just as much as the side facing the earth. It should more correctly be referred to as the far side of the Moon or lunar far side.
dark sky – Pertaining to a night sky that is relatively free of light pollution. Obviously, the darker the sky, the better the view of the stars.
Dark Sky – A company that produces weather apps for smart phones. In this case, the term dark sky refers to the dark clouds that occur around heavy thunderstorms and other bad weather, and has nothing to do with the dark skies at night time.
dark-sky compliant – Unfortunately, there is no standard that defines outdoor light fixtures that are dark-sky compliant. Various manufacturers use different standards to denote which of their products are compliant. The closest thing to a standard are the set of protocols. developed by the International Dark Sky Association (IDA), the Fixture Seal of Approval Program.
dark-sky friendly – A product that minimizes glare, reduces light trespass, and minimizes skyglow.
DarkSky International – A non-profit organization whose goals are to build awareness of the value of dark skies, and of the need for quality outdoor lighting. Formerly known as the International Dark-Sky Association (IDA).
dark-sky movement – A campaign consisting of citizens helping to reduce light pollution and preserving the view of the stars at night.
daylight – See light bulb color ranges.
diffuser – A device used to distribute light from a source.
dimmer – A device used to reduce the input power, thereby reducing the output level of incandescent, fluorescent, and LED lights. Fluorescent and LED lights sometimes need special dimmers in order to work.
disability glare – Glare resulting in reduced visual performance and visibility. It is often accompanied by discomfort.
discharge lamp – See gas-discharge lamp.
discomfort glare – Glare that produces discomfort, but does not necessarily diminish visual performance.
downlight – A luminaire in which the light output is directed downward. Downlights can be recessed, surface-mounted, or pendant.
driver – An electronic device that transforms the main supply voltage into the lower DC voltage needed for LEDs and CFLs. Some lamps have a built-in driver, while others require a driver to be connected externally.
E
eclipse – The blocking of the light of one celestial body by another.
efficacy – The ratio of light emitted to the amount of energy used, measured in lumens per watt (lm/W). It is the number of lumens output by the bulb per watt of energy input. It is sometimes called luminous efficacy.
efficiency – The amount of light energy produced by a light bulb compared to the electrical energy that it uses. Unlike LED bulbs, most of the energy used by an incandescent bulb is converted to heat rather than light. Efficiency is the percentage of output divided by input. Inefficient bulbs waste energy and produce less light.
electromagnetic (EM) radiation – Energy in the form of electromagnetic waves that travels through space at the speed of light. The total range of electromagnetic wavelengths and frequencies is called the electromagnetic spectrum. The types of electromagnetic radiation include radio, microwave, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, x-rays, and gamma-rays. Human eyes are only sensitive to the small portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that we call visible light.
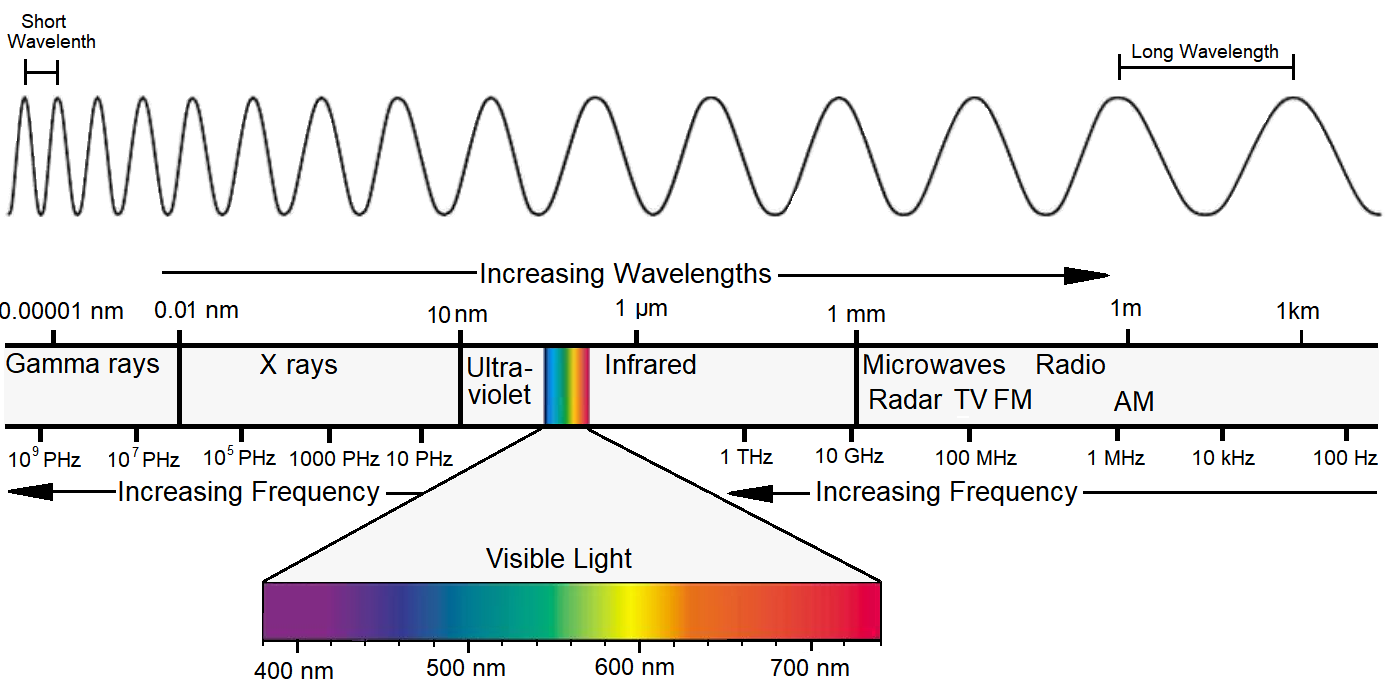 electromagnetic (EM) spectrum – The full range of electromagnetic radiation, with wavelengths from longest to shortest, or frequencies from lowest to highest. Astronomers use instruments that can observe as much of the electromagnetic spectrum as possible to learn about the nature and history of the universe.
electromagnetic (EM) spectrum – The full range of electromagnetic radiation, with wavelengths from longest to shortest, or frequencies from lowest to highest. Astronomers use instruments that can observe as much of the electromagnetic spectrum as possible to learn about the nature and history of the universe.
EM – ElectroMagnetic. See electromagnetic radiation or electromagnetic spectrum.
energy – the ability of a system to perform work. The unit for energy is the joule, the energy required to move an object 1 meter against a force of 1 newton, or the kilowatt-hour (kWh). In the US the non-metric unit for energy is the foot-pound, which equals 1.355 joules. See also power.
 Energy Star – A program for energy savings and sustainability developed by the US Department of Energy and Environmental Protection Agency. To be Energy Star rated, a product must have energy performance among the top 25% of all products of its type. Energy Star products must be certified by an independent third-party to provide increased energy efficiency. If the product costs more than a similar non- Energy Star product, the purchaser must be able to recoup his/her investment through utility savings.
Energy Star – A program for energy savings and sustainability developed by the US Department of Energy and Environmental Protection Agency. To be Energy Star rated, a product must have energy performance among the top 25% of all products of its type. Energy Star products must be certified by an independent third-party to provide increased energy efficiency. If the product costs more than a similar non- Energy Star product, the purchaser must be able to recoup his/her investment through utility savings.
extinction coefficient – A measure of the rate of reduction of transmitted light due to scattering and absorption in a medium.
F
façade lighting – The illumination of the exterior of a building
field angle – See beam angle.
fixture – See luminaire.
fixture lumens – A light fixture’s light output after processing of emitted light by optics in that fixture.
Fixture Seal of Approval Program – A program established by the IDA to certify lighting products that are night-sky friendly.
fixture watts – The total power consumed by a fixture. This includes the power consumed by the lamp(s) and ballast(s).
floodlight – A fixture designed to “flood” a well defined area with light.
fluorescent lamp – A discharge lamp, usually tubular in shape, where the light is produced by passing a current through mercury vapor to produce ultraviolet light. The tubes have a coating of fluorescent material on their inner surface that causes it to emit visible light.
flux – The action or process of flowing, such as energy flux being the flow of energy. See luminous flux.
footcandle – Illuminance produced on a surface one foot from a uniform light source of one candela. One foot-candle equals one lumen per square foot.
footlambert – The average luminance of a surface emitting or reflecting light at a rate of one lumen per square foot.
full-cutoff fixture – Defined by the IES as “Zero intensity at or above horizontal (90° above nadir) and limited to a value not exceeding 10% of lamp lumens at or above 80°.”
fully shielded fixture – A fixture that allows no emission above a horizontal plane through the fixture.
G
gas-discharge lamp – A lamp in which light is produced by sending an electrical discharge between two electrodes within a gas. Discharge lamps include fluorescent lamps, which usually have internal coatings to convert the ultraviolet energy emitted by the gas discharge into visible light, and LPS lamps. Sometimes called discharge lamps or gas-discharge arc lamps. See also HID lamp.
glare – Intense and blinding light that reduces visibility. A light within the field of vision that is brighter than the brightness to which the eyes are adapted.
H
halogen lamp – An incandescent lamp having of a tungsten filament sealed in a transparent bulb that is filled with a mixture of an inert gas and a small amount of a halogen, such as iodine or bromine. The halogen gas and the tungsten filament produces a halogen cycle chemical reaction which redeposits evaporated tungsten back onto the filament, increasing its life and maintaining the clarity of the bulb. However, a halogen lamp must be operated at a much higher temperature than a standard incandescent lamp of similar power. It also produces light with higher luminous efficacy and color temperature. Both standard and halogen incandescent bulbs are much less efficient than LED and compact fluorescent lamps, and, as a result, have been banned in many jurisdictions. Also known as a tungsten halogen lamp, quartz-halogen lamp, or quartz iodine lamp.
heat sink – A component of a lamp or luminaire used to dissipate heat. Heat sinks typically use materials with a high thermal conductivity and have a fin-like geometry to maximize the contact of their surface with the air.
HID – High-Intensity Discharge (HID). See HID lamp.
high-intensity discharge (HID) lamp – A discharge lamp that produces a high-intensity light ouput. HID lamps include mercury vapor, metal halide, and high pressure sodium lamps.
high-pressure sodium (HPS) lamp – An HID lamp lamp where light is produced by passing a current through sodium vapor under a relatively high pressure.
house-side shield – Opaque material applied to a fixture to block the light from illuminating a residence or other structure being protected from light trespass.
I
IDA – See DarkSky International.
IES – Illuminating Engineering Society.
IESNA – Illuminating Engineering Society of North America.
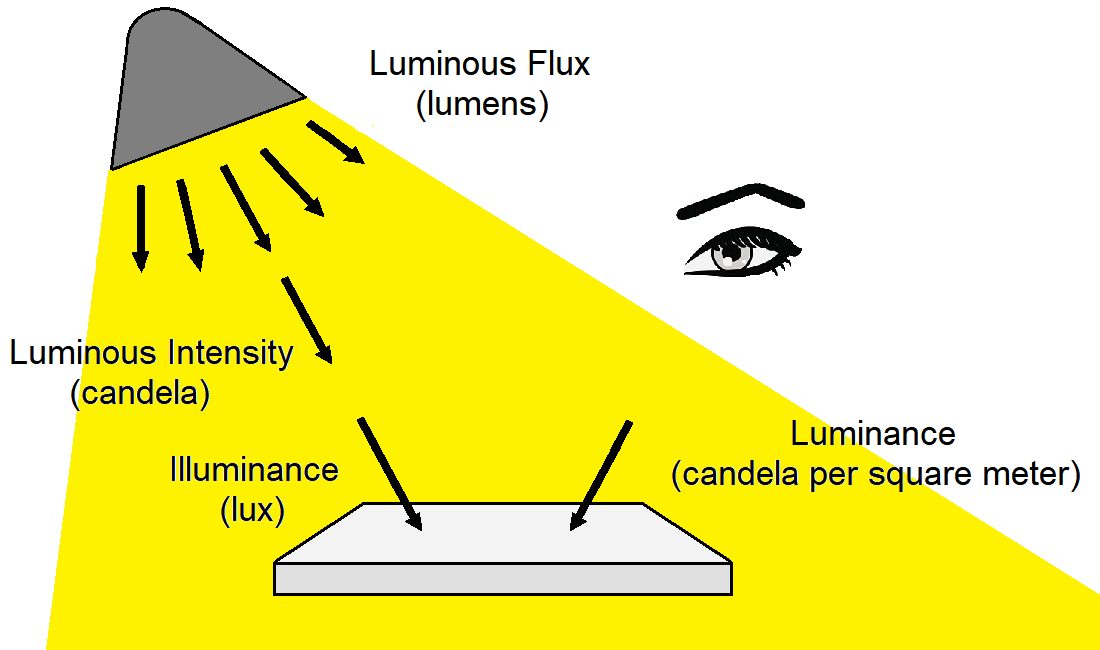 illuminance – The total luminous flux incident on a surface, per unit area. It measures how much the incident light illuminates the surface, wavelength-weighted to correlate with human perception of brightness, measured in lux (lx). If you illumiunate a surface, the amount of light being projected towards it by the light is illuminance. Compare with luminance, which is the amount of light reflected from the surface being illuminated. To help remember which is which, remember that illuminance begins with IL (incident light) and measures incident light. Luminance begins with L (leaving) and is the light that is leaving. Illuminance was formerly called brightness, but due to confusion with other uses of the word, it was replaced by illuminance. Brightness should not be used for quantitative description, but only for as references to perceptions of light.
illuminance – The total luminous flux incident on a surface, per unit area. It measures how much the incident light illuminates the surface, wavelength-weighted to correlate with human perception of brightness, measured in lux (lx). If you illumiunate a surface, the amount of light being projected towards it by the light is illuminance. Compare with luminance, which is the amount of light reflected from the surface being illuminated. To help remember which is which, remember that illuminance begins with IL (incident light) and measures incident light. Luminance begins with L (leaving) and is the light that is leaving. Illuminance was formerly called brightness, but due to confusion with other uses of the word, it was replaced by illuminance. Brightness should not be used for quantitative description, but only for as references to perceptions of light.
Illuminating Engineering Society of North America (IES or IESNA) – The professional society of lighting engineers, including those from manufacturing companies, and others professionally involved in lighting.
incandescent lamp – Light is produced by a filament heated to a high temperature by electric current.
infrared radiation – Electromagnetic radiation with longer wavelengths than those of visible light, extending from the nominal red edge of the visible spectrum at 700 nanometers to 1 millimeter.
intensity – The strength or amount of light produced by a specific lamp.
International Dark-Sky Association (IDA) – See DarkSky International.
inverse-square law – Illuminance at a point varies directly with the intensity (I) of a point source and inversely as the square of the distance (d) to the source. E = I / d2
J
joule (J) – the unit for energy, work, or heat. It is equal to the force, energy, or work done by applying a force of one newton through a distance of one meter (1 newton-meter), or about 1⁄3600 of a watt. It is also equal to the of energy needed to pass an electric current of one ampere through a resistance of one ohm for one second (1 watt-second). In the US the non-metric unit for energy is the foot-pound, which equals 1.355 joules. One BTU of heat is approximately 1,055 joules.
K
 Kelvin scale – A temperature scale in which its zero point is absolute zero, the temperature at which all thermal motion stops, -273.16° Celsius or -459.67°Fahrenheit. Until 1967, the unit on this scale was a degree Kelvin (°K) and was the same size as a degree Celsius (°C). In 1967, the term “degree” was dropped and the absolute temperature unit was redefined as the kelvin (K). The Kelvin Color Scale uses this unit. See Kelvin Color Scale.
Kelvin scale – A temperature scale in which its zero point is absolute zero, the temperature at which all thermal motion stops, -273.16° Celsius or -459.67°Fahrenheit. Until 1967, the unit on this scale was a degree Kelvin (°K) and was the same size as a degree Celsius (°C). In 1967, the term “degree” was dropped and the absolute temperature unit was redefined as the kelvin (K). The Kelvin Color Scale uses this unit. See Kelvin Color Scale.
kilowatt-hour (kWh) – A unit of energy equal to the work done by one kilowatt (1,000 watts) of power acting for one hour. 1,000 watt-hours (Wh).
L
lamp – See light bulb.
lamp life – The average life span for a specific type of lamp, determined as the number of hours in which half of a large number of lamps will fail or burn out. The actual life of any given lamp will typically be different from the average life span. Also called average rated life.
LED – Light Emitting Diode.
light – See visible light or light bulb.
light bulb – A device that produces light when an electric current is passed through it. There are several types of light bulbs, including incandescent bulbs, CFL bulbs, flourescent bulbs, and LED bulbs. Sometimes called a lamp or a light.
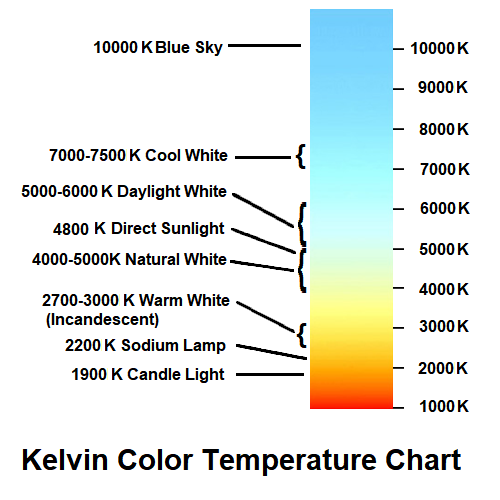
light bulb color ranges – Names given by lighting manufacturers for ranges of CCT. The names and ranges vary from one manufacturer to another, and sometimes overlap. The names should be used only as a guide and choice of color should be made using the actual CCT value. The term daylight refers to a artificail light that is supposed to simulate actual daylight. The color of natural daylight is 5600 K on a sunny day at noon.
Light Bulb Color Ranges |
|||
Name |
Alternate Names |
CCT |
Color Range |
| Soft White | Cool White | 2700 K - 3000 K | Yellowish |
| Warm White | Cool White | 3000 K - 4000 K | Yellowish to White |
| Bright White | Neutral White Warm White |
4000 K - 5000 K | White to Blue |
| Daylight | 5000 K - 6500 K | Blue | |
light emitting diode (LED) – a semiconductor device that emits visible light in a variety of colors when a voltage is applied to it.
lighting facts – Manufacturers of consumer lighting products are now required to provide labels with certain information on their packaging, which is called lighting facts. See examples.
light fixture – See luminaire.
light fitting – See luminaire.
lighting controls – Devices used for either turning lights on and off or for dimming. Photocell sensors are used to turn lights on and off in response to natural light levels. Some advanced mode can slowly dim or increase the lighting. See also adaptive controls.
light intensity – See brightness or intensity.
light output – See brightness.
light pollution – The adverse effect of artificial light, which has a disruptive effect on natural cycles and inhibits the observation of stars and planets.
light quality – A measurement of a person’s comfort and perception based on the lighting.
light spill – Unwanted spillage of light onto adjacent areas and may affect sensitive receptors particularly residential properties and ecological sites.
light trespass – Light that crosses property boundaries and is visible from locations off the property where it is not wanted.
light year – A unit of distance used in astronomy equal to the distance light travels in one year, or about 5.85 trillion miles or 9.46 × 1012 km.
low-pressure sodium (LPS) lamp – A discharge lamp where the light is produced by passing a current through sodium vapor at a relatively low pressure.
lumen (lm) – The unit of luminous flux, equal to the amount of light emitted per second in a unit solid angle of one steradian from a uniform light source of one candela.
lumen depreciation factor – Light loss of a luminaire with time due to the lamp decreasing in efficiency, dirt accumulation, and any other factors that lower the effective output with time.
luminaire – A complete lighting assembly consisting of one or more lamps together with the housing, the parts designed to control light output, such as a reflector (mirror) or refractor (lens), the parts to position and protect the lamps, the ballast (if required), and a connection to the power supply. Also known by the less technical terms of light fixture (US) and light fitting (UK).
luminaire efficiency – The ratio of the light emitted by the luminaire compared to the light emitted by the enclosed lamps.
 luminance – The amount of light emitted, passed through, or reflected from a surface for a given solid angle, measured in candela per square meter (cd/m2). Compare with illuminance, which is the amount of light being projected toward the surface being illuminated. To help remember which is which, remember that illuminance begins with IL (incident light) and measures incident light. Luminance begins with L (leaving) and is the light that is leaving.
luminance – The amount of light emitted, passed through, or reflected from a surface for a given solid angle, measured in candela per square meter (cd/m2). Compare with illuminance, which is the amount of light being projected toward the surface being illuminated. To help remember which is which, remember that illuminance begins with IL (incident light) and measures incident light. Luminance begins with L (leaving) and is the light that is leaving.
luminous efficacy – See efficacy.
luminous intensity – A measure of the power emitted by a light source in a particular direction per steradian (unit solid angle), that is wavelength-weighted based on the sensitivity of the human eye, using the candela (cd).
luminous flux – A measure of the total amount of light a lamp puts out in all directions, that is wavelength-weighted based on the sensitivity of the human eye, measured in lumens. Also called luminous power.
lux (lx) – Unit of illuminance, equal to one lumen per square meter.
M
magnitude – A measure of the brightness of an object in the sky used in astronomy. The scale is logarithmic and each step of one magnitude changes the brightness by a factor of the fifth root of 100, approximately 2.512. For example, a magnitude 1 star is exactly 100 times brighter than a magnitude 6 star. The brighter an object appears, the lower the value of its magnitude. The brightest objects can have negative values.
mercury lamp – An HID lamp where light is produced by passing a current through mercury vapor.
metal-halide lamp – An HID lamp where the light is produced by passing a current through metal-halide vapors.
meter (m) – (1) The unit of length in the metric system, equal to approximately 39.37 inches. Larger and smaller units are defined by using prefixes, such as 1 kilometer (km) = 1,000 m, 1 centimeter (cm) = 0.01 m, 1 millimeter (mm) = 0.001 m, and 1 nanometer (nm) = 0.000000001 m. (2) An instrument used to measure and indicate a quantity. Light meters and sky quality meters are examples used in measuring light.
motion sensors – A lighting control system that senses movement. There are two types of sensors: passive infrared and ultrasonic. Passive infrared sensors use infrared beams to sense motion. When beams of infrared light are interrupted by movement, the sensor turns on the lighting system. If no movement is sensed after a predetermined period, the system turns the lights off. Ultrasonic sensors use high-frequency sound waves pulsed through a space to detect movement. When the frequency of the sound waves change, the sensor turns on the lighting system. After a predetermined time with no movement, the system turns the lights off. Sometimes called occupancy sensors.
mounting height – The height of the fixture or lamp above the ground.
N
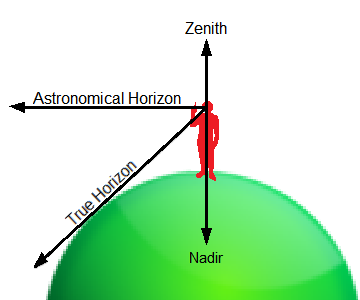 nadir – A point on the celestial sphere directly below the observer, diametrically opposite the zenith.
nadir – A point on the celestial sphere directly below the observer, diametrically opposite the zenith.
nanometer (nm) – One billionth of a meter (10‑9 m). Often used as the unit for wavelength in the EM spectrum.
narrow-band amber LED (NBALED) lamp – A type of outdoor lighting that uses an LED that produces primarily yellow-amber colored light directly, without using a phosphor like that used in PCALED lights. They are very efficient. However, they can experience significant thermal instability, causing light output to diminish over time. Because they are a relatively new technology, these lamps are not widely available and, therefore, are still relatively expensive.
NBALED – Narrow-Band Amber LED.
NELM – Naked Eye Limiting Magnitude. A determination of the quality of the night sky by using visual observations to determine the magnitude of the faintest stars than can be observed visually with the naked eye near the zenith. The main criticism of this technique is that observations vary somewhat from observer to observer. Note that lower numbers indicate brighter stars. Here is what NELM observations indicate:
Magnitude |
Description |
| 6.3 | Indicates significantly degraded sky quality |
| 6.6 | Considered near pristine under average conditions |
| 7.0 | Achievable under good seeing conditions with proper dark adaptation of the eye |
| 7.4 | Excellent, just about the faintest attainable |
neutral white – See light bulb color ranges.
nm – Abbreviation for nanometer.
O
occupancy sensors – See motion sensors.
optic – The components of a luminaire, such as reflectors (mirrors), refractors (lenses), and protectors, which make up the light emitting section.
optcal spectrum – See visible light.
ordinance – A rule or regulation passed by a municipality, such as a city, town, or village, which (in Texas and most states) has the same force as any other law, within its city limits. Of particular interest to the dark-sky proponents is ordinances that regulate outdoor lighting.
outdoor lighting – Lights used to illuminate outdoor areas at night, usually for safety, decoration, or advertisement. Outdoor lighting includes, but is not limited to, street lights, parking lot lighting, residential lighting, landscaping, and billboards and other signs.
P
PCALED – Phosphor-Converted Amber LED.
phosphor-converted amber LED (PCALED) lamp – A type of outdoor lighting that uses an LED that produces blue light, but contains a nitride phosphor to convert the light to a longer wavelength. This type of lamp produces amber light much more efficiently than using LEDs that produce amber light directly.
photometry – The quantitative measurement of light level and distribution.
photocell – An electronic device that changes the light output of a luminaire dynamically in response to the ambient light level around the luminaire.
planet – A celestial body that moves in an elliptical orbit around the sun or a star.
power (P) – (1) The measurement of the ability to produce work per unit time, measured in watts. One watt equals one joule per second. Power also equals volts times amperes. In the US, watts is often used to measure power, but other forms of power are measured using horsepower (hp), where 1 horsepower is about 745.7 watts. (2) The rate at which energy is produced, measured in watts. (3) The electricity supply that provides energy to appliances and other electric devices. In the US, household power is usually alternating current at 60 Hz and 110 volts. Other countries use various combinations of 110 or 220 volts at 50 or 60 Hz.
Q
quality of light – A subjective ratio of the pluses to the minuses of any lighting installation.
quartz halogen lamp – See halogen lamp.
quartz iodine lamp – See halogen lamp.
R
radian (rad) – A unit for measuring angles. One radian is the angle made at the center of a circle by an arc whose length is equal to the radius of the circle. It is equal to approximately 57.3°. See also steradian.
radiation – See electromagnetic radiation.
reflector – An optic that achieves control of light by means of reflection (using mirrors).
refractor – An optic that achieves control of light by means of refraction (using lenses).
S
 semi-cutoff fixture – Defined by the IES as “Intensity at or above 90° (horizontal) no more than 5% of lamp lumens and no more than 20% at or above 80°”.
semi-cutoff fixture – Defined by the IES as “Intensity at or above 90° (horizontal) no more than 5% of lamp lumens and no more than 20% at or above 80°”.
shielding – An opaque material that blocks the transmission of light.
skyglow – Diffuse, scattered sky light attributable to scattered light from sources on the ground.
Sky Quality Index (SQI) – An index, ranging from 0 to 100, used to express the distribution sky glow caused by artificial light. The distribution of sky glow is determined using the entire sky, with only horizon obstructions masked out. SQI values indicate the following:
SQI |
Description |
| 100 | A sky free of artificial sky glow |
| 80 - 100 | Skies with all of the natural characteristics throughout most of the sky |
| 60 - 80 | Skies with most of the natural features only within 40 degrees of the zenith |
| 40 - 60 | Skies where the Milky Way is not visible or only visible near the zenith |
| 20 - 40 | Skies with only stars and planets remaining and the land is illuminated at a level of moonlight |
| 0 - 20 | Skies where only the brightest stars remain and the land is in perpetual twilight |
sky quality meter – Unihedron sky quality meter.
soft white – See light bulb color ranges.
source intensity – This applies to each source in the potentially obtrusive direction, outside of the area being lit.
spill light – Light that illuminates surfaces beyond the area intended to be illuminated.
spotlight – A fixture designed to light only a small, well-defined area.
SQI – Sky Quality Index.
SQM – Sky Quality Meter.
square radian – See steradian.
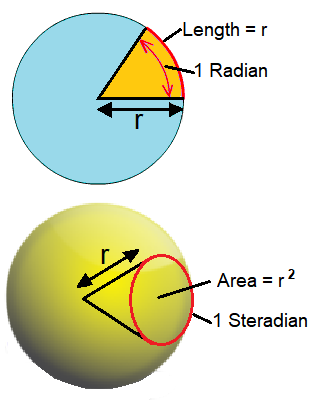 star – A self-luminous object that shines in the night sky by the release of energy produced by nuclear reactions at its core, the same as the sun.
star – A self-luminous object that shines in the night sky by the release of energy produced by nuclear reactions at its core, the same as the sun.
steradian (sr) – The unit of solid angle, used in three-dimensional geometry. It is analogous to the radian that is used with two-dimensional angles. An angle in radians projected onto a circle gives a length on the circumference, but a solid angle in steradians projected onto a sphere gives an area on the surface. Also known as a square radian.
stray light – Emitted light that falls away from the area where it is needed or wanted. Light trespass.
T
task lighting – Task lighting is used to provide direct light for specific activities without illuminating the entire area.
tungsten halogen lamp – See halogen lamp.
U
ultraviolet (UV) light – A type of electromagnetic radiation that is not visible to the human eye, having a wavelength just below visible light, between 100 nm and 400 nm. Also called ultraviolet radiation.
ultraviolet radiation – See ultraviolet light.
Unihedron sky quality meter (SQM) – An instrument designed to measure the luminance of the night sky, typically used by amateur astronomers. It measures the skyglow aspect of light pollution in units of magnitudes per square arcsecond. SQM measurements can be submitted to a database on Unihedron's website and to the citizen science project GLOBE at Night.
UV – UltraViolet. See ultraviolet light.
V
veiling luminance – A luminance produced by bright sources in the field-of-view superimposed on the image in the eye reducing contrast and hence visibility.
visibility – Being perceived by the eye. Seeing effectively. The goal of night lighting.
visible frequencies – See visible light.
visible light – The range of electromagnetic radiation that can be detected by the human eye, wavelengths of about 380 nm to 800 nm. Also called visible frequencies, visible spectrum, or the optical spectrum.
visible spectrum – See visible light.
W
wallpack – A luminaire, typically affixed to the side of a structure, used for area lighting.
warm white – See light bulb color ranges.
watt (W) – A unit for measuring electrical power. It is defined as one joule per second, and is used to express the rate wat which energy is converted or transferred. One watt is also the rate at which work is done when one ampere of current flows through an electrical potential difference of one volt.
watt-hour (Wh) – A unit of energy equivalent to one watt (W) of power expended for a period of one hour. The energy of 1 Wh is equivalent to 3,600 joules (J).

X - Y - Z
zenith – A point in the sky directly above the observer. It is the highest point on the celestial sphere, the opposite of the nadir, the lowest point on the sphere.
References
International Dark-Sky Association. “Glossary” http://www.darksky.org/our-work/grassroots-advocacy/resources/glossary/, accessed 06/01/2019.
Los Senderos Studio. “Glossary” https://lossenderosstudio.com/glossary.php, accessed 06/01/2019.
FLOS. “Glossary” https://usa.flos.com/glossary, accessed 06/01/2019.
Good Earth Lighting. “Glossary” http://www.goodearthlighting.com/glossary, accessed 06/05/2019.
Flagstaff Dark Skies Coalition. “Glossary” http://www.flagstaffdarkskies.org/glossary/, accessed 06/10/2019.
McDonald Observatory. “Glossary” https://mcdonaldobservatory.org/glossary, accessed 06/05/2019.
National Park Service. “Night Sky Monitoring Report Metrics & Glossary of Terms” https://www.nps.gov/subjects/nightskies/skydata.htm, accessed 06/10/2019.
Parmar, Jignesh. “What is Fixture's Beam Angle & Beam Diameter (Part-1)” https://electricalnotes.wordpress.com/2018/06/23/what-is-fixtures-beam-angle-beam-diameter-part-1/, accessed 06/14/2019.

